In 2021, the United States witnessed a grim milestone with 48,830 gun-related deaths, underscoring stark disparities influenced by gun ownership rates, political ideologies, and demographic factors. States like Mississippi, Louisiana, New Mexico, Alabama, and Wyoming recorded the highest rates of gun deaths, each surpassing 25 deaths per 100,000 people. Mississippi topped the list with 33.9 deaths per 100,000, reflecting significant regional variations in gun violence.
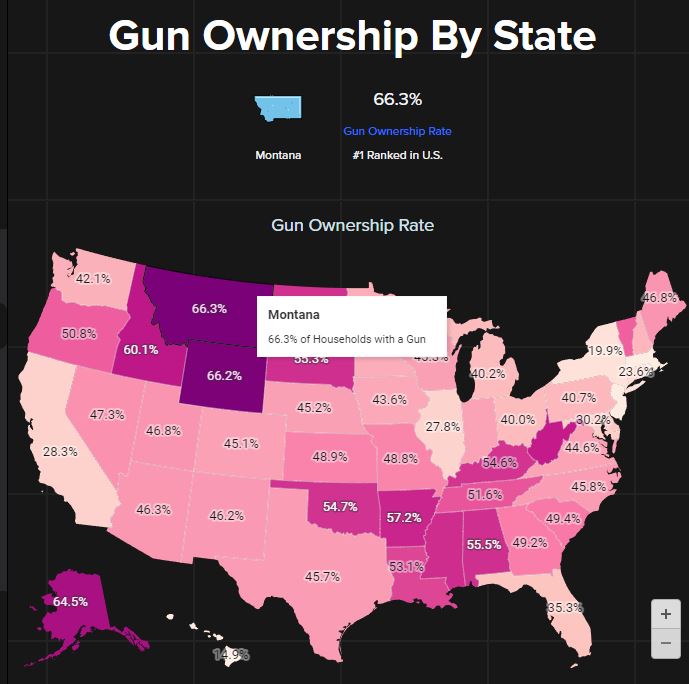
States with higher rates of gun ownership often correlate with increased gun-related fatalities. For example, Wyoming, known for both high gun ownership and a high death rate, illustrates this connection. Conversely, states with lower gun ownership rates, such as Massachusetts and New Jersey, tend to report fewer gun deaths, highlighting the impact of stricter firearm regulations.
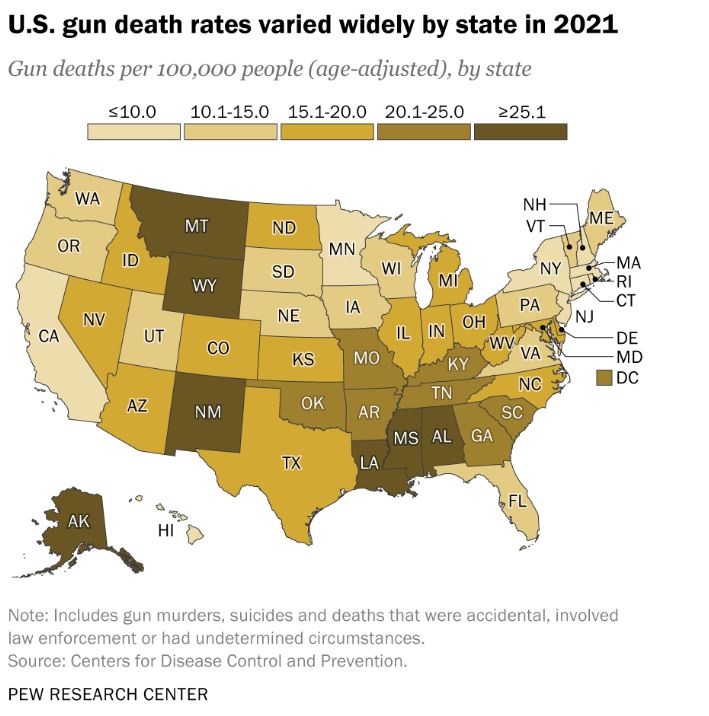
Political leanings play a crucial role in shaping gun policy and outcomes. States governed by Republican leadership, where there is typically more support for Second Amendment rights and less stringent gun control measures, tend to experience higher rates of gun deaths. This trend is evident in states like Mississippi and Alabama, where cultural norms around firearms ownership contribute to elevated fatality rates.
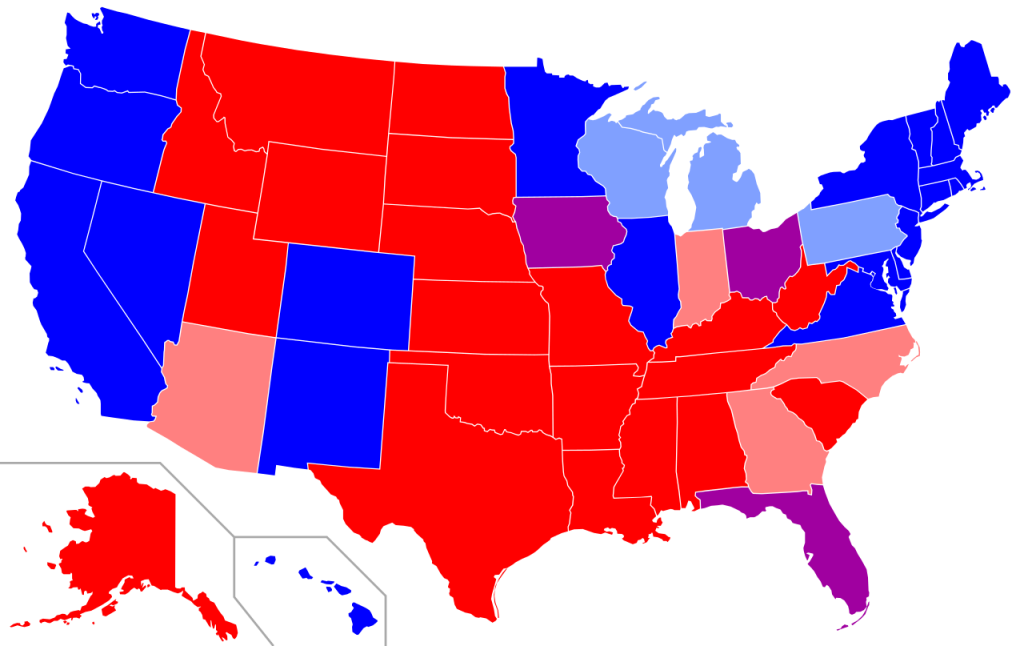
The Supreme Court’s pending decisions on Second Amendment cases could have profound implications for states with historically lower rates of gun violence. If the Court rules in favor of broader interpretations of the Second Amendment, states controlled by Democratic leadership may face pressures to relax existing gun control measures. This potential shift could lead to an increase in gun violence as regulations are loosened.
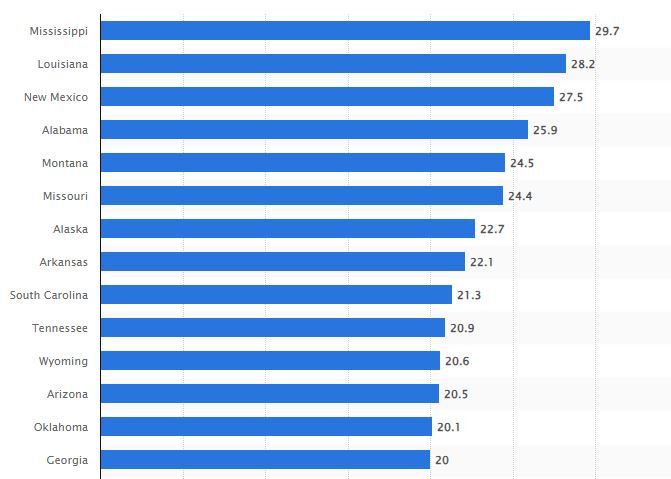
New Mexico stands out as an outlier in gun death statistics, with a rate of 27.8 deaths per 100,000 people in 2021. This can be partly attributed to its demographic composition, including a significant military presence, which influences gun prevalence and related fatalities. Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty levels and access to mental health services, also contribute significantly to variations in gun death rates among states.
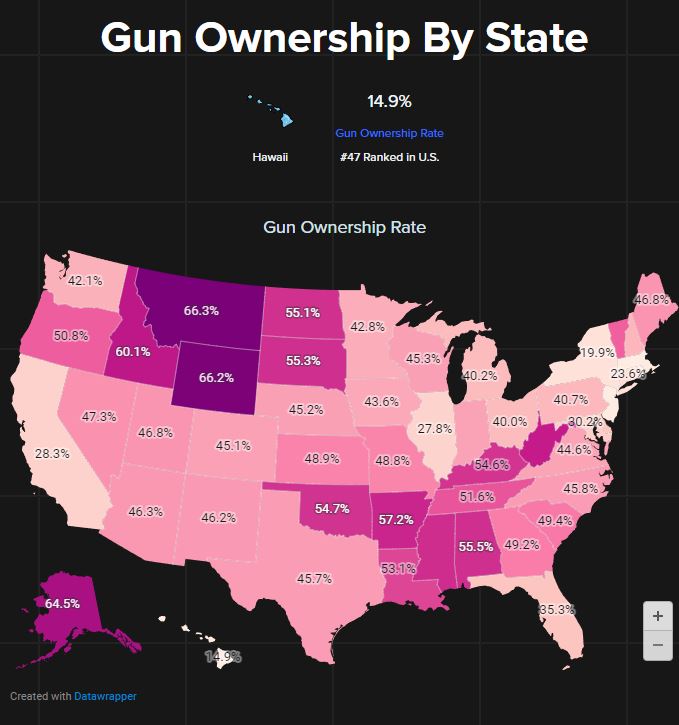
Wyoming, with its high gun ownership rates and Republican governance, exemplifies a state where firearms are deeply ingrained in the culture, alongside less stringent gun control measures. In contrast, Massachusetts, governed by Democrats and with lower gun ownership rates, has implemented strict gun laws and prioritized public health initiatives aimed at reducing gun-related fatalities.

Legislative challenges persist in states with high rates of gun deaths, where the balance between Second Amendment rights and public safety remains contentious. Advocates for stricter regulations emphasize the need for enhanced public safety measures, while opponents argue for preserving individual rights to firearm ownership.

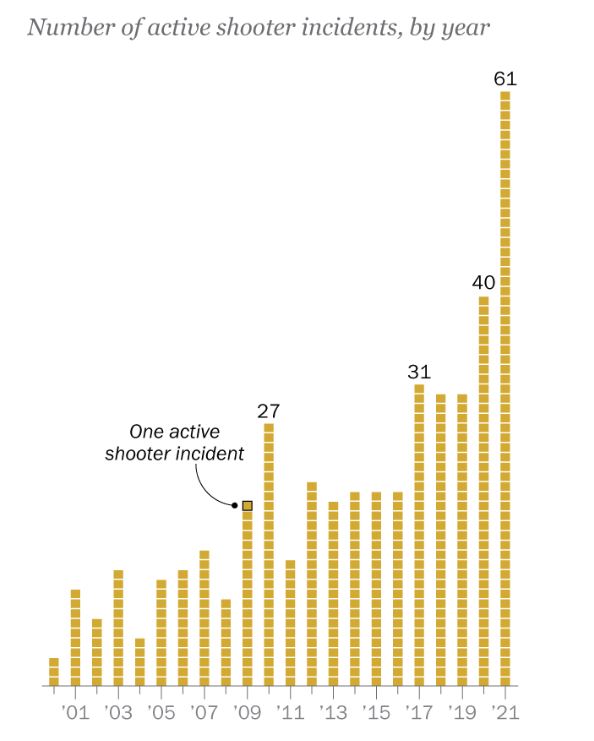
Effective strategies to address gun deaths require comprehensive community engagement, mental health support, and evidence-based interventions. States must adopt holistic approaches that integrate legislative measures with efforts to tackle underlying socioeconomic disparities contributing to gun violence.
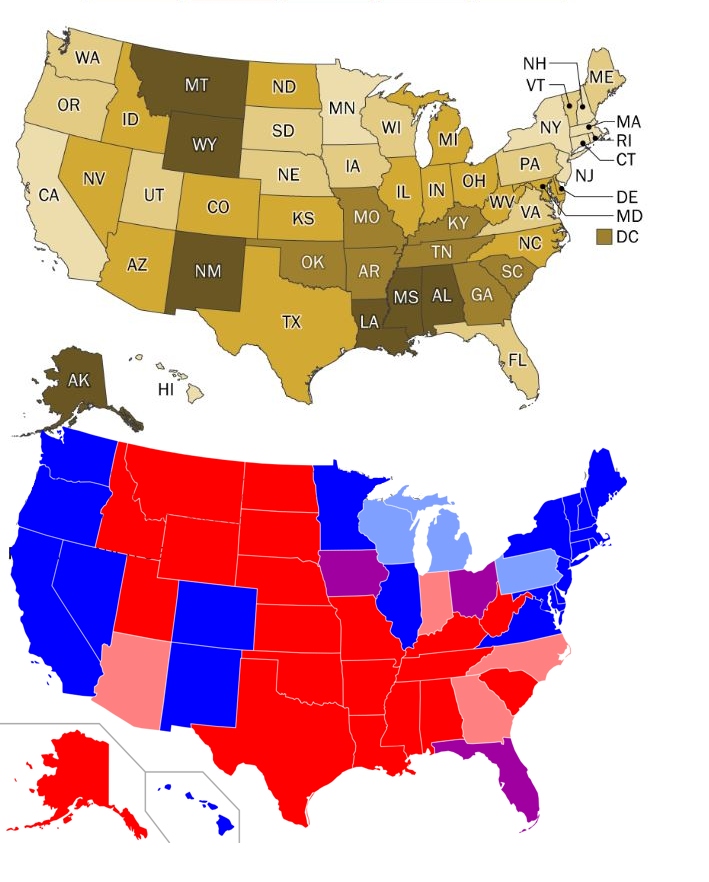
The correlation between gun ownership rates, political leanings, and gun-related fatalities is evident across the United States. States governed by Republican leadership, characterized by higher rates of gun ownership and less restrictive gun laws, tend to report higher levels of gun-related deaths. As the nation navigates these challenges, informed dialogue, evidence-based policy-making, and proactive public health initiatives are crucial to reducing the impact of gun violence and fostering safer communities nationwide.

The outcomes of pending Supreme Court cases on the Second Amendment could significantly influence the trajectory of gun control laws in the United States. Currently before the court is whether or not individuals with stocking orders for domestic violence can legally own firearms. These decisions have the potential to reshape state-level regulations, impacting future trends in gun-related fatalities and shaping the landscape of gun policy across the country.




