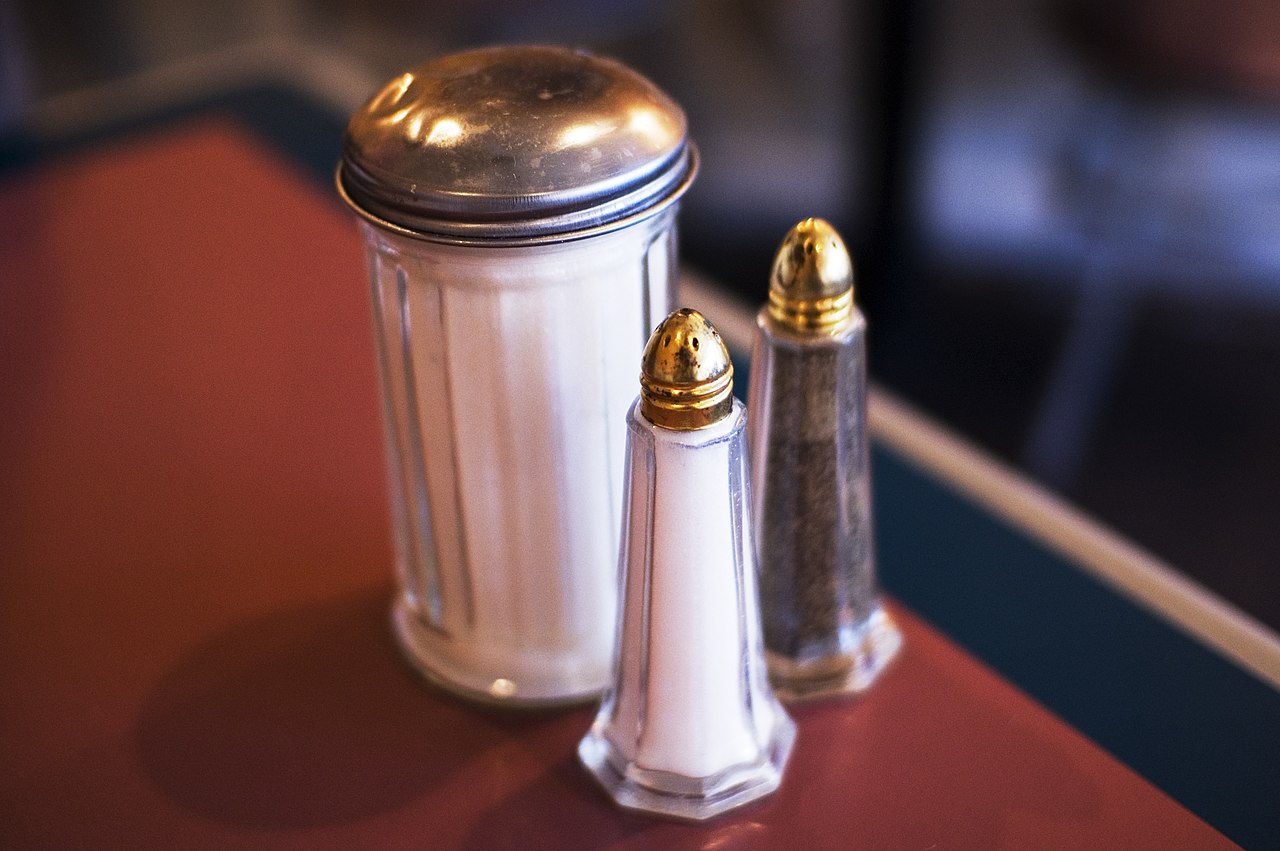
Using too much salt might increase your chances of getting stomach cancer, according to a study by nutritionists at the University of Vienna. They found that people in the UK who regularly added salt to their meals were 41 percent more likely to develop stomach cancer compared to those who used less salt. This is one of the first studies to show this link in Western countries.

Salt is everywhere, and many of us don’t realize how much we’re actually eating. The FDA suggests we should have no more than one teaspoon of salt per day, but the average American ends up consuming about 50% more than that. Even seemingly harmless foods like canned soup can contain a lot of salt. Using too much salt regularly can be harmful, the researchers warn.
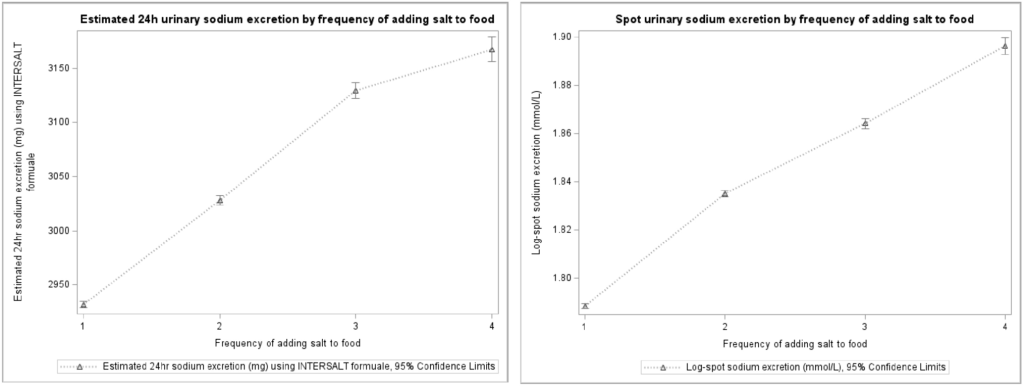
The study looked at data from over 470,000 adults in the UK over 11 years. They found that those who used a lot of salt were still more likely to get stomach cancer even after considering other factors like age and lifestyle choices such as drinking and smoking, which are also linked to stomach cancer.
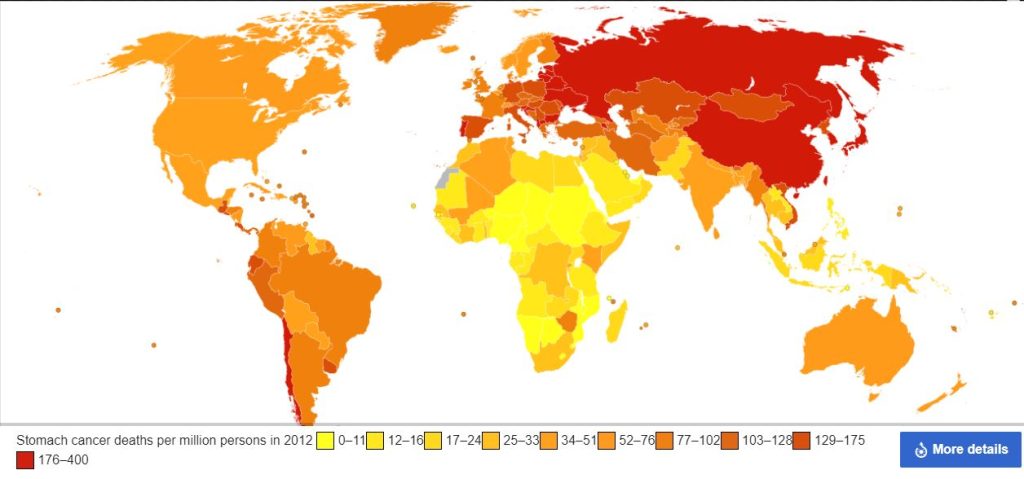
Stomach cancer is a serious concern. In 2024 alone, around 27,000 new cases are expected in the US, resulting in over 10,000 deaths. Catching it early gives you a better chance of survival, but symptoms can be easy to miss, like bloating or upset stomach, which many people may mistake for normal discomfort.

Researchers hope to raise awareness about the risks of consuming too much salt, so people can take steps to reduce their chances of developing stomach cancer. By understanding these risks, we can make healthier choices for ourselves.
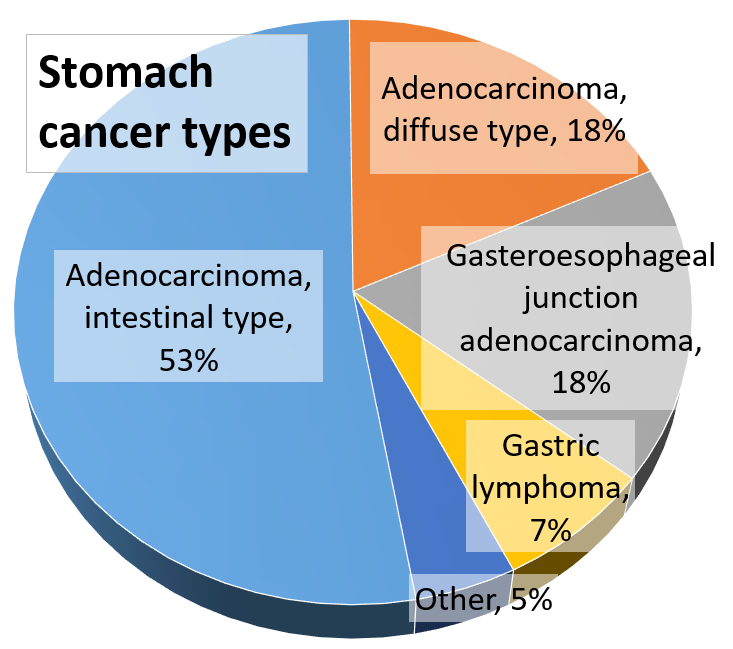
One way to understand the study’s findings is by looking at the impact of salt on our bodies. Excessive salt consumption can damage the protective lining of the stomach over time, potentially leading to cancerous changes in the stomach tissue. This damage can occur even in Western populations, not just in countries where salty diets have long been associated with stomach cancer.

It’s important to note that salt isn’t inherently bad; our bodies need it to function properly. However, it’s the excess salt that poses a risk to our health. Being mindful of how much salt we add to our meals and choosing low-sodium alternatives can help reduce our risk of developing stomach cancer and other related health issues.

Ultimately, this study highlights the importance of paying attention to our dietary habits and their potential impact on our health. By making informed choices and moderating our salt intake, we can take proactive steps towards promoting our well-being and reducing the risk of serious health conditions like stomach cancer.






