In a concerning development, two feral pigs discovered in Calaveras County, California, have been found to be carrying a potentially lethal virus, raising alarms about the safety of pets in the area. The United States Department of Agriculture identified the presence of the Peudorabies (PRV) virus in samples taken from these pigs, within a 10-mile radius of Burson, according to a spokesperson from the Calaveras Health and Human Services Agency.

Peudorabies (PRV) poses a significant risk to pets, particularly dogs and cats, with transmission typically occurring through contact, bite wounds, or the consumption of raw feral pig meat. As a precautionary measure, the infected pigs were euthanized to prevent further spread of the virus.

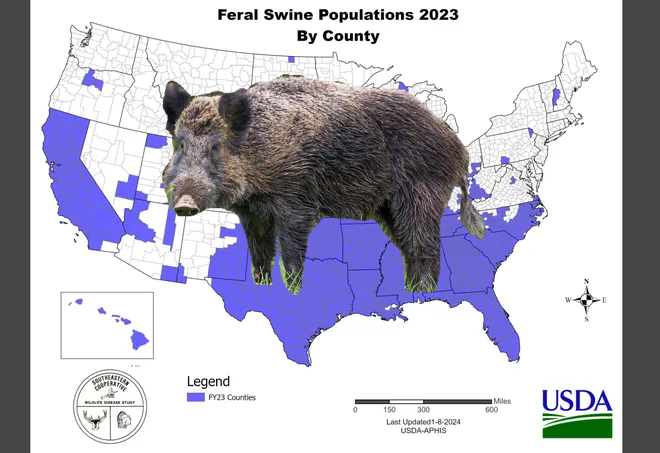
This discovery underscores the ongoing challenges posed by feral pigs across the United States. Despite efforts to control their population, an estimated 6 to 9 million feral swine continue to cause significant damage nationwide, with total annual damages estimated at a minimum of $2.5 billion.
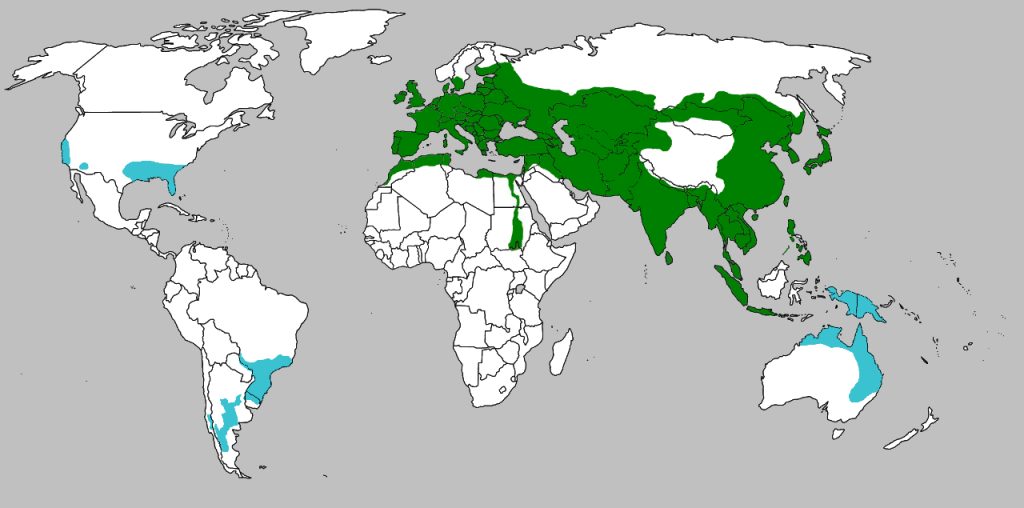
Feral pigs, known for their destructive behavior, have become a multibillion-dollar plague on farmers, wildlife, and the environment. Originating from wild boars brought to the Americas by early European settlers, these animals have since spread rapidly, adapting to various habitats and climates.
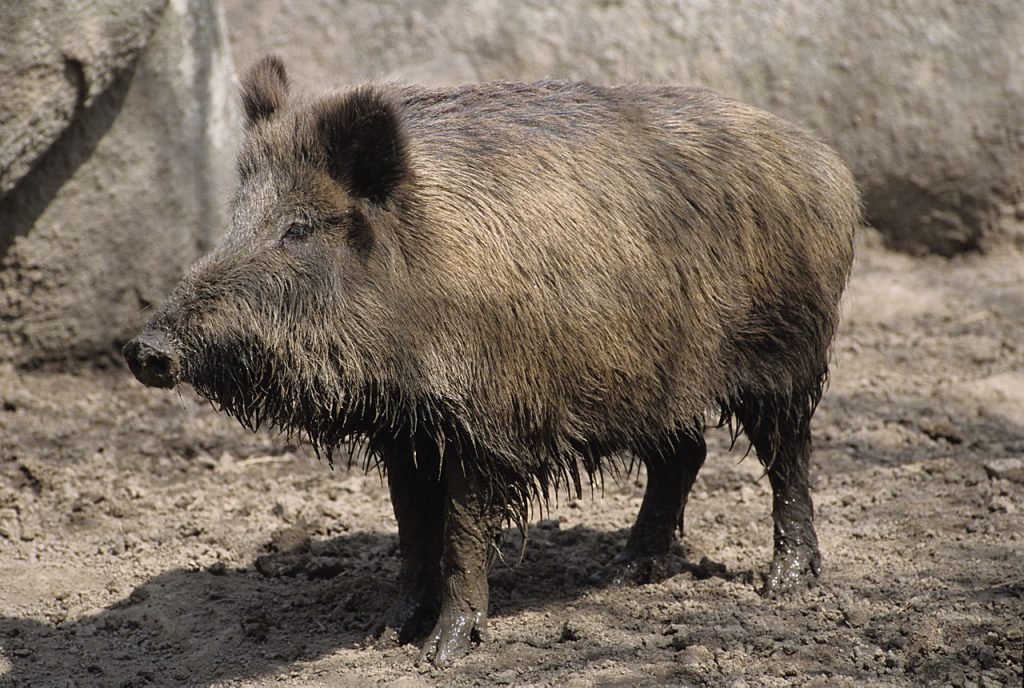

In recent years, the proliferation of feral hogs has extended beyond their traditional range, with sightings reported in at least 35 states. From the marshlands of Florida to the farmlands of Texas, feral pigs have become a ubiquitous presence, posing threats to agriculture, ecosystems, and public safety.
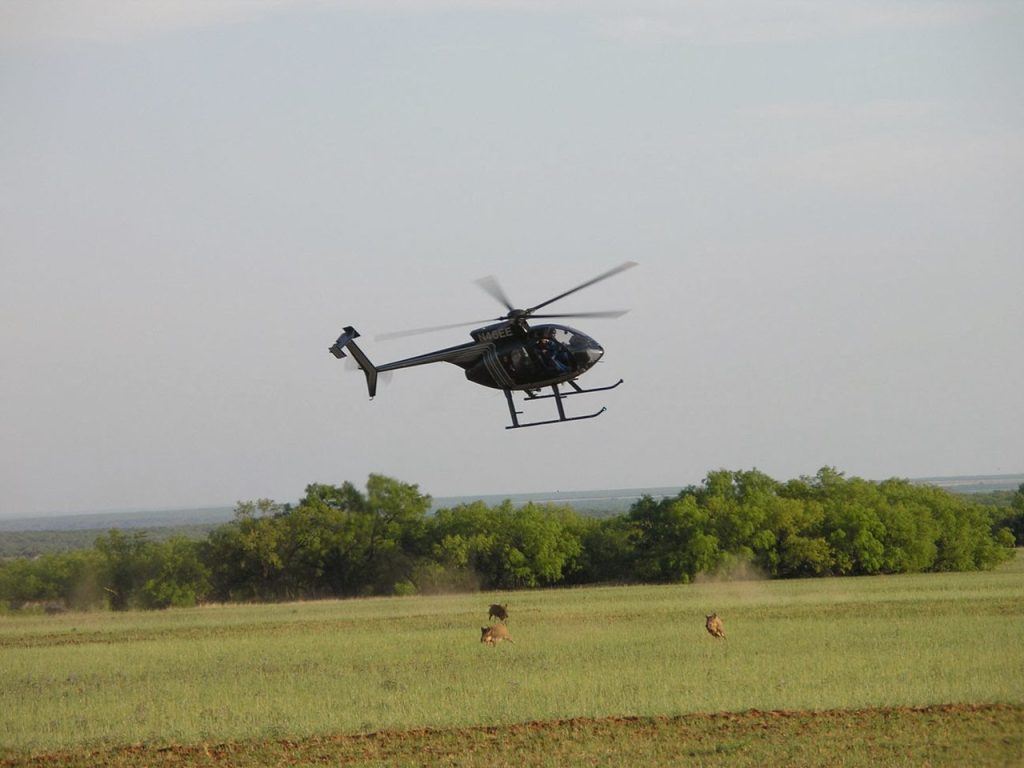

Efforts to manage the feral hog population vary widely across states, with methods ranging from hunting to lethal removal. However, the challenge persists, as these resilient animals continue to outpace control efforts, reproducing rapidly and adapting to new environments.
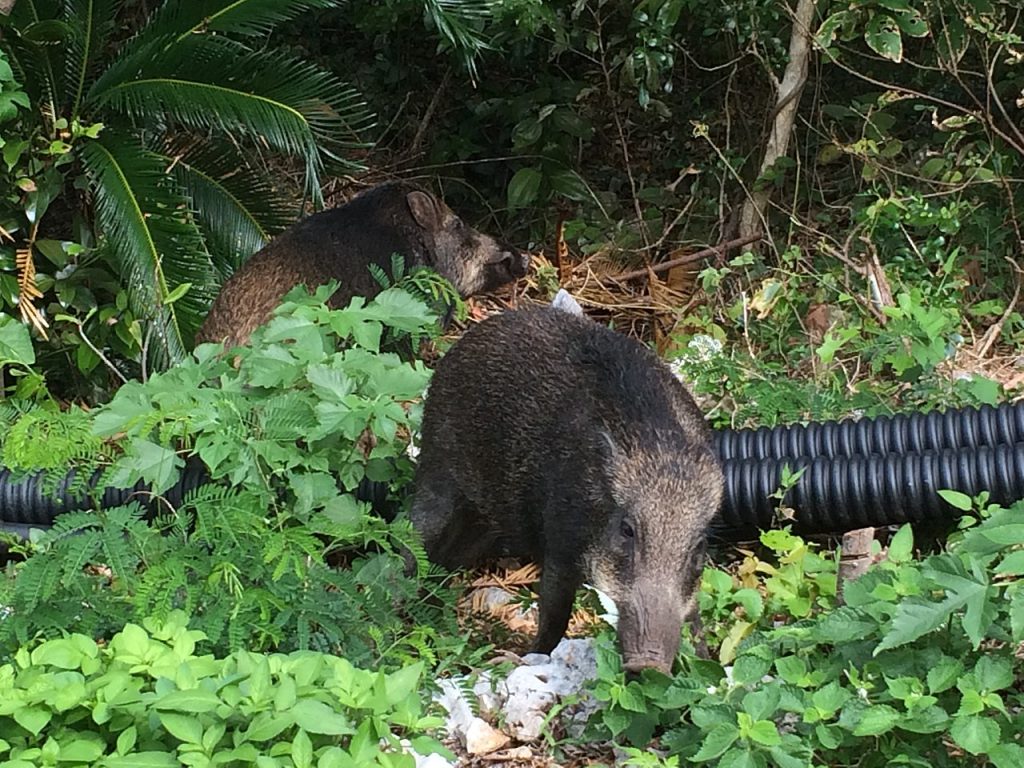

The debate over the environmental impact of feral hogs continues, with some arguing that they contribute to native plant diversity and nutrient availability.
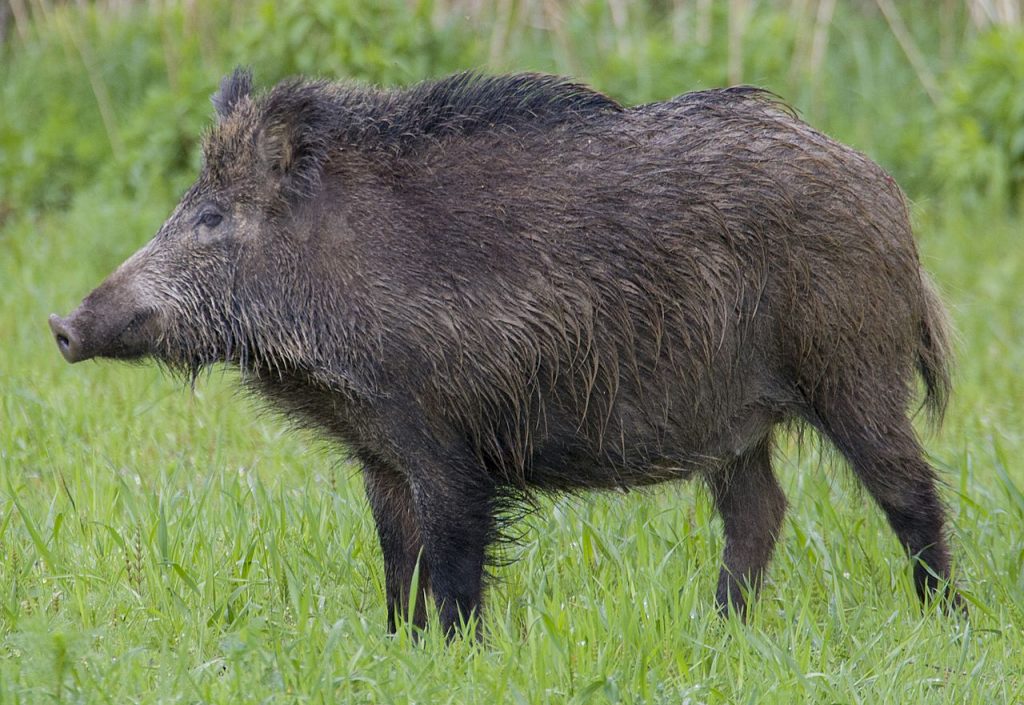

However, most experts agree that their overall impact is detrimental, leading to significant economic losses and environmental degradation.

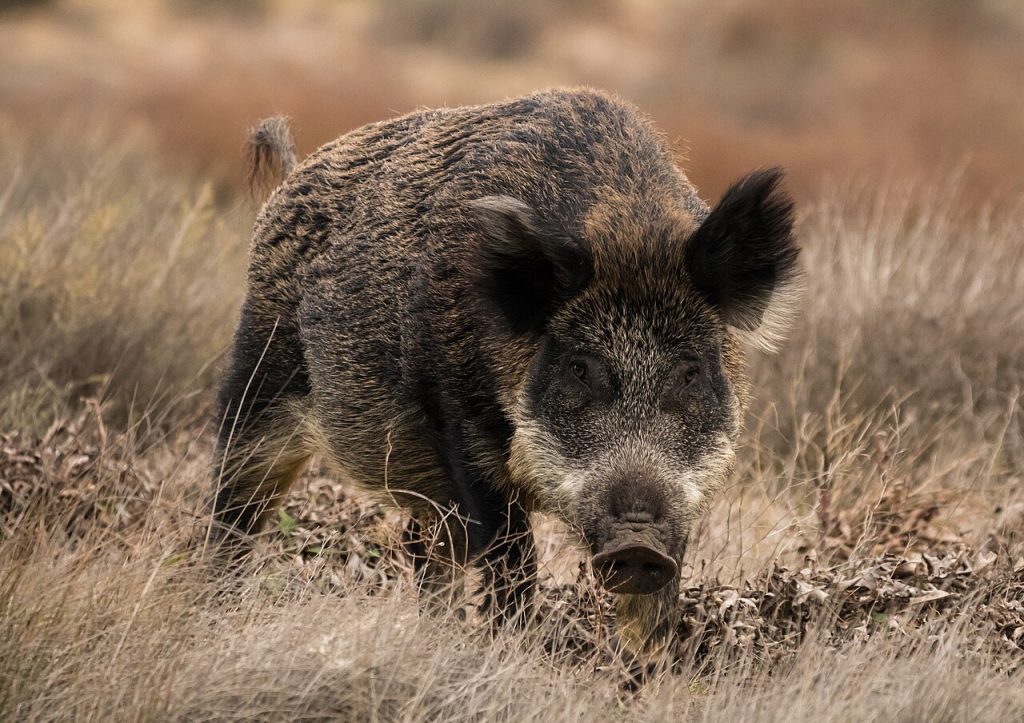
In addition to the challenges posed by feral pigs, concerns about diseases like African Swine Fever loom large, threatening to devastate the U.S. pork industry if introduced.

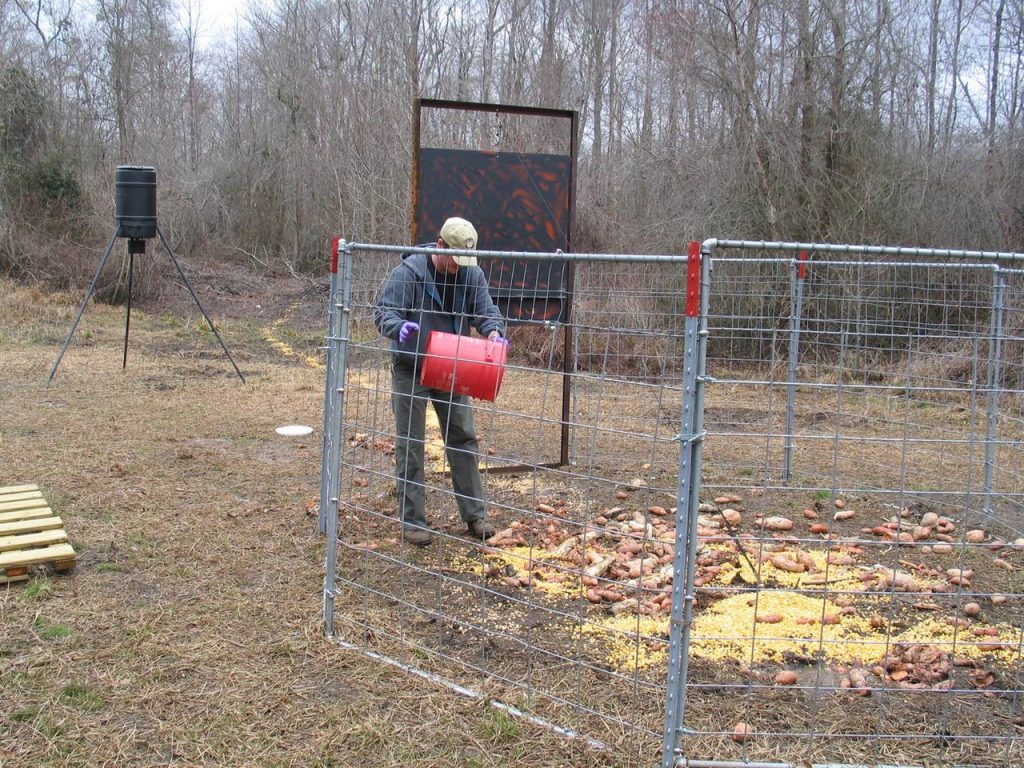
While efforts are underway to explore alternative solutions such as oral contraceptives, the need for effective management strategies remains paramount. Human removal is carried out by trapping the hogs using bait as seen above.
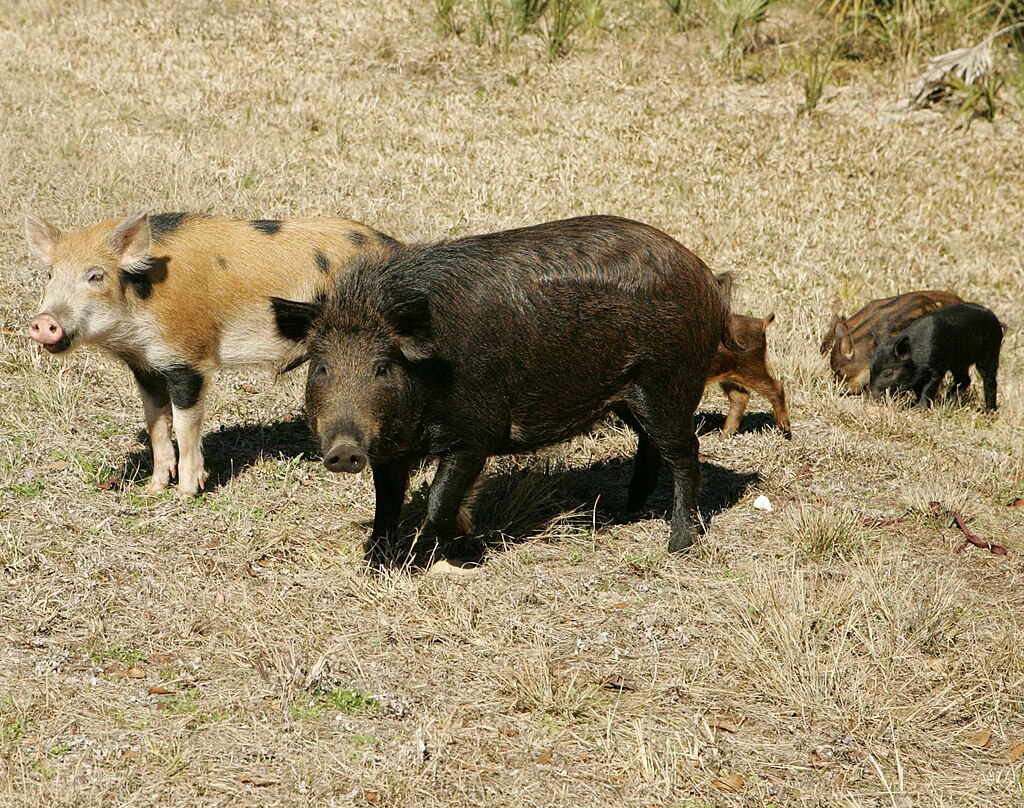

As communities grapple with the growing feral hog problem, residents are urged to remain vigilant and take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their pets. With ongoing research and coordinated efforts, addressing the threat posed by feral pigs remains a priority for agricultural and environmental authorities alike.